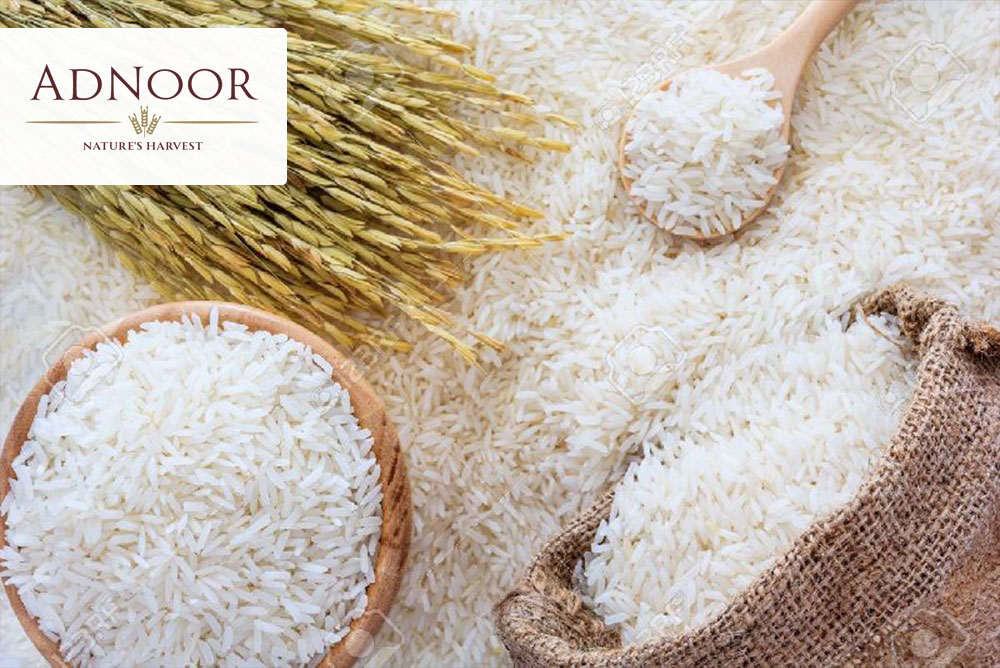
Rice is a starchy rich in carbohydrates. This cereal has many benefits. Note, however, that the more the rice is husked, refined, treated, polished, and very white, the less fibre, vitamins and of minerals.
Nutritional Quality of Rice: Caloric Intake and Proteins
For developing countries, rice represents about 27% of energy intake and up to 60% for more than 2 billion Asians. Its caloric value is equivalent to that of wheat: around 350 kcal/100 g (1,400 to 1,500 kilojoules).
Rice is lower in protein than wheat: 8 to 9%, while wheat provides 12%. As with other cereals, rice does not contain all the essential amino acids; two are absent: lysine and cystine.
A Carbohydrate-Rich Starch
Rice is a supplier of complex carbohydrates (78%) in the form of starch (amyloidosis and amylopectin).
The higher the amylose content, the longer the grains will remain loose and have increased in size and volume. Conversely, rice low in amylose and high in amylopectin will give so-called “sticky” or “glutinous” rice. Rice is very low in lipids (0.5 to 1%).
Rice Is A Source Of Vitamins B1 And B2 And Is Rich In Minerals.
Brown rice is a source of B1 vitamins (thiamine) and B2, which are important for the nervous system. A deficiency in vitamin B1 (beriberi) has been observed in populations that eat white rice. Parboiled rice is richer in vitamins because the process promotes the migration of vitamins and mineral salts to the heart of the grains.
The minerals like potassium, iron, phosphorus, and magnesium (about 1%) are unevenly distributed in the different layers of the grain. It is also an important source of riboflavin, niacin and fibres.
The various treatments of rice influence the nutritional value of the latter. The more it is peeled, refined, treated, polished, and white, the less fibre, vitamins and minerals it contains.
Health: Rice, Gluten-Free Food That Promotes Constipation
- Rice can be eaten by everyone.
- White rice and rice cooking water are constipating; they are used in case of diarrhea.
- Rice does not contain gluten.
- Its low salt and fat content makes it suitable for diets.
- The portion is 50-60 g of raw rice per person. Rice absorbs about three times its volume in water.
- In 1995, the Codex Alimentarius Commission endorsed quality and safety standards for rice intended for human consumption.
Rice Grain Structure, Composition and Quality Criteria
The grain of rice (paddy) consists of a protective covering (husk) and a caryopsis or fruit (brown rice or husked rice)
Brown rice includes the outer layers of the pericarp, the tegument and the nucellus, as well as the germ, or embryo, and the albumen (the endosperm). The albumen includes the albumen proper and the aleurone layer; it covers the embryo. Their pigmentation is limited to the pericarp.
The weight is distributed as follows in brown rice:
- pericarp: 1 to 2%;
- aleurone plus nucellus and integument: 4 to 6%;
- germ: 1%;
- scutellum: 2%;
- albumen: 90 to 91%.
The aleurone comprises one to five layers of cells. It is thicker on the dorsal side than ventral and thicker in short-grain rice than in long-grain rice.
The cells of the aleurone and the embryo are rich in proteins and lipids
The endosperm cells have a thin membrane and are filled with amyloplasts containing starch granules. The two outermost cell layers are rich in protein and lipids, and the amyloplasts and compound starch granules are smaller in size there than in the inner albumen.
Starch granules are polyhedra. The proteins are present there in spherical form throughout the albumen. Crystalline protein bodies and spherical protein bodies are located in the sub-aleuron layer.
Non-glutinous rice (containing amylose in addition to amylopectin) has translucent albumen, while glutinous rice (0-2% amylose) has opaque albumen due to the presence of pores between the starch granules and the interior thereof. Therefore, the weight of glutinous rice grain is about 95-98% of that of non-glutinous rice grain.
Impurity tolerances are as follows for milled rice:
- organic extraneous matter: 0.5%;
- inorganic extraneous matter: 0.1%;
- immature kernels: 2.0%;
- damaged kernels: 3.0%;
- heated grains: 3.0%;
- red seeds: 4.0%;
- grains streaked with red: 8.0%;
- chalky grains: 11.0%.
The proposed tolerances for parboiled milled rice are identical to those for milled rice, with some exceptions.
Starch
Starch is the main component of milled rice, making up about 90 % of the dry matter. It is a polymer of glucose D alpha-(1-4) bond, and it consists of a linear moiety, amylose, and a branched moiety, amylopectin. The branch points are alpha-(1-6) bonds. The affinity of rice amylopectin for iodine stands at 0.4-0.9%.
Based on calorimetric standards of absorption of iodine-starch from 590 to 620 nm, milled rice is classified as follows (Juliano, 1979, 1985b):
- waxy: 1 to 2%;
- very low amyloidosis: 2 to 12%;
- low amyloidosis: 12 to 20%;
- intermediate amyloidosis: 20 to 25%;
- high amyloidosis: 25 to 33%.
Proteins
The proteins of the endosperm (milled rice) consist of the following:
- 15% albumin (water soluble);
- globulin (soluble in salts);
- 5 to 8% prolamin (soluble in alcohol);
- glutelin (soluble in alkalis).
The lysine content of rice protein is 3.5-4%, and rice bran proteins are richer in albumin than albumen proteins.
Lipids
The fat content of rice is mainly in the bran (20% dry matter), but milled rice contains between 1.5 and 1.7% fat, mostly in the form of non-starch fat. Essential fatty acid content may increase directly with temperature during grain development, but at the cost of a decrease in total oil content.
Non-Starch Polysaccharides
The polysaccharides non-starch consist of water-soluble polysaccharides and insoluble dietary fibre. They can combine with starch and may have a hypocholesterolemic effect. Albumen has a lower dietary fibre content than other brown rice constituents.
Milled rice endosperm has a low lignin but a high content of pectin.
Volatile Compounds
The characteristic volatile compounds of cooked rice are ammonia, hydrogen sulphide and acetaldehyde. When cooked, all the rice aromatic contains 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline as the main aromatic principle. The volatile compounds characteristic of the rancidity of materials fat are the aldehydes, in particular hexanol and ketones.
Visit the ADNOOR website for the best golden Sella basmati rice, long-grain rice, brown rice, Super Kernel Basmati Rice, white rice, nuts, seeds, and dried fruits. We take pride in saying that we are the Best Basmati rice suppliers in Montreal and have been the importers, exporters, wholesalers, distributors, and co-packers of various nuts and grains in Canada for the last 25 years. We aim to provide our customers with quality products, so they keep trusting us. So without wasting time, visit our website and order what you need.